|
Remarkable in many respects radio-source Sagittarius B2 was investigated
in HI radio-line at wavelength 21 cm, OH lines at frequencies 1665 and
1667 MGz and H2CO absorption line at wavelength 6.2 cm.
These data have allowed us to create the dynamic model of the cloud
of gas, around this object.
The cloud of gas of diameter 40 pc rotates with the velocity 20 km/s
at it`s edge and therefore it is stable. For its stabilization
mass part 2.5E+5 mass of Sun is required, that corresponds
to data of the CO observations.
The results on H2CO absorption lines (figure 1) have shown,
that the central part of the cloud represents a clumped envelope
of diameter 9 pc with radial velocity 20 km/s.
The relation of radial velosity of absorption line and the whole
object have allowed simple to define the direction of radial movement
- itis compression. The total mass of it cloud - 5.5E+5 mass of the Sun.
Measured kinematic parameters have allowed to determine the
following script of development of this area of formation of stars :
approximately 2E+7 years this cloud was stable with diameter, twice
large then observable, after the part of the turbulent energy has
converted due to warm to the magnetic viscosity, approximately
5E+5 years ago began the compression in regime of free fall.
2.5E+5 years ago the fragmentation and the formation of stars began.
We note, that gas cloud compression is the direct observational
confirmation of the standart way of formation of stars.
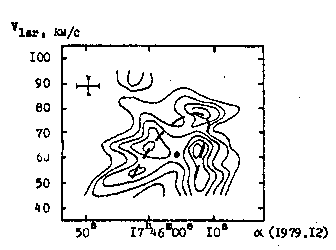 Figure 1. The distribution of H2CO absorption line in radio-source
Sagittarius B2.The strokes show contracting semienvelope.
Figure 1. The distribution of H2CO absorption line in radio-source
Sagittarius B2.The strokes show contracting semienvelope.
|
