|
We present the results of computation of linear diameter, density and HI mass spectra for about 5000 HI clouds, which were found by their emission at 21 cm with RATAN-600 radio telescope in the region of 180 degree < l < 260 dg. and -15 dg.< b < +15 dg. The spectra were corrected for selection effects. The diameter spectrum has an approximately power shape with spectral index of -3.0 +- 1. A density spectrum in the range of 1.0 to 500 cm-3 is not a power form, but has a maximum at nH = 20 - 60 cm-3 depending of galactic latitude. The mass spectrum in the form of M X N(log M) was obtained in the mass range of 0.6 to 2.5 X 104 mass of the Sun. It consists of at least three parts.
These data show that in the middle mass range the process of coalescence in cloud-cloud collisions predominates but the clouds with low masses are evaporated probably due to very hot ISM component. In the very high mass range the number of clouds may be decreased because of gravitational instability. 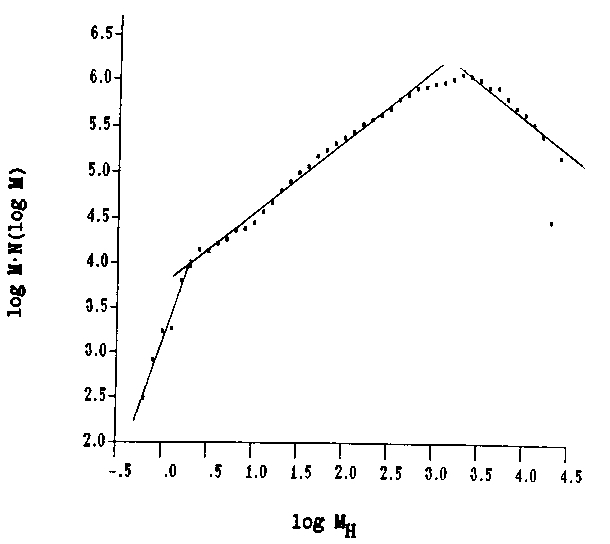
Figure 1. The mass spectrum in the form of M X N(log M) was obtained in the mass range of 0.6 to 2.5 X 104 masses of the Sun. |