Main Stellar Spectrograph of the BTA
3. Instrumental capabilities of the spectrograph
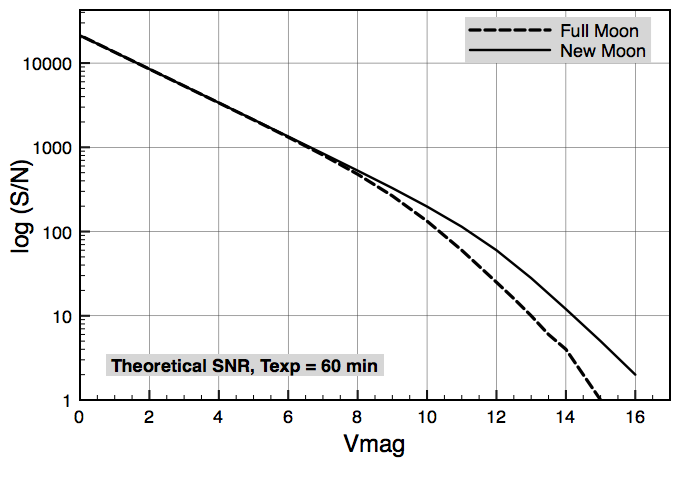

Fig. 7. Theoretical optical resolving power of the MSS, depending on the phases of the moon under typical weather conditions.
Fig. 7. Theoretical optical resolving power of the MSS, depending on the phases of the moon under typical weather conditions.
The optical resolving power of the telescope with the MSS allows to observe stars of up to the 12 magnitude. The graph in Fig. 7 gives an idea about the spectrograph capabilities in the observations of faint point sources.
Currently, more than 90% of observational time with the MSS spectrograph is used in the spectropolarimeter mode with a diffraction grating 24.7°. An order registers a 550 Å –wide spectral region with a reciprocal linear dispersion of 9 Å/mm (0.1215 Å/pix) at a time. In the second spectral order the dispersion amounts to 13.5 Å/mm (0.1823 Å/pix).
Signal-to-noise value calculator (Javascript)
These calculations are performing for the observational conditions: seeing 1.2-1.5″, z = 20°; the circular polarization analyzer in conjunction with an image slicer is in use. The order of dispersion and a grating angle are given to help the observer choosing the right settings.



