News archive
2025
-
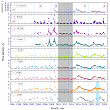 Six- and Two-Year Quasi-Periods of Long-Term Variability of the Blazar AO 0235+164 Determined for the First Time from Multiwavelength Observations. More...
Six- and Two-Year Quasi-Periods of Long-Term Variability of the Blazar AO 0235+164 Determined for the First Time from Multiwavelength Observations. More... -
 Detection of Depression Effects in Radio Emission from the Solar Corona. More...
Detection of Depression Effects in Radio Emission from the Solar Corona. More... -
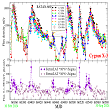 Detection of Five Giant Flares from Microquasar Cyg X-3 in 2024. More...
Detection of Five Giant Flares from Microquasar Cyg X-3 in 2024. More...
2024
-
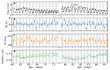 Cygnus X-3 revealed as a Galactic ultraluminous X-ray source by IXPE. More...
Cygnus X-3 revealed as a Galactic ultraluminous X-ray source by IXPE. More...
2023
-
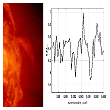 Detection of the hydroxyl (OH) absorption line in the radio emission of the solar corona. More...
Detection of the hydroxyl (OH) absorption line in the radio emission of the solar corona. More... -
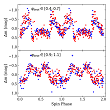 New asynchronous polar discovered. More...
New asynchronous polar discovered. More... -
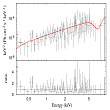 Discovery of the first candidate ultraluminous X-ray source with a neutron star with a field of 1012 G in a 1 billion-year-old star cluster. More...
Discovery of the first candidate ultraluminous X-ray source with a neutron star with a field of 1012 G in a 1 billion-year-old star cluster. More... -
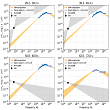 Detection and study of the optical flare that accompanied GRB 210619B, and the object model. More...
Detection and study of the optical flare that accompanied GRB 210619B, and the object model. More... -
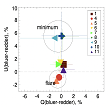 Detection of color variability of the optical polarization of the blazar BL Lac. More...
Detection of color variability of the optical polarization of the blazar BL Lac. More... -
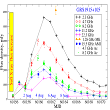 Multi-frequency studies of the giant radio burst of the Black hole X-ray binary GRS 1915+105 at time scale from 9 minutes to 9 days More...
Multi-frequency studies of the giant radio burst of the Black hole X-ray binary GRS 1915+105 at time scale from 9 minutes to 9 days More... -
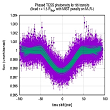 Planet TOI1408.01: a grazing transit and probably a highly eccentric orbit. More...
Planet TOI1408.01: a grazing transit and probably a highly eccentric orbit. More... -
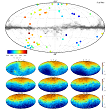 The LMC impact on the kinematics of the Milky Way satellites: clues from the running solar apex. More...
The LMC impact on the kinematics of the Milky Way satellites: clues from the running solar apex. More...
2022
-
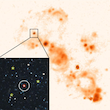 Unveiling Unusual Nitrogen-rich Massive Star in Metal-poor Dwarf Galaxy. More...
Unveiling Unusual Nitrogen-rich Massive Star in Metal-poor Dwarf Galaxy. More... -
 Peekaboo: the “hidden” extremely metal poor dwarf galaxy. More...
Peekaboo: the “hidden” extremely metal poor dwarf galaxy. More... -
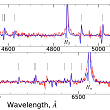 Luminous Blue Variables (LBVs) are a rare type of massive stars with high luminosity and strong photometric and spectral variability. Clarification of the nature and evolutionary status of LBVs requires a significant expansion of the sample of the known and studied stars of this type. More...
Luminous Blue Variables (LBVs) are a rare type of massive stars with high luminosity and strong photometric and spectral variability. Clarification of the nature and evolutionary status of LBVs requires a significant expansion of the sample of the known and studied stars of this type. More... -
 Now there is no doubt that the activity of galactic nuclei is associated with a central supermassive black hole. The matter captured by the black hole forms a rotating accretion disk. More...
Now there is no doubt that the activity of galactic nuclei is associated with a central supermassive black hole. The matter captured by the black hole forms a rotating accretion disk. More... -
 The modernization of the instruments and software complex of the MANIA experiment for searching for and studying the variability of astrophysical objects with a temporal resolution of 10−6s has been completed. More...
The modernization of the instruments and software complex of the MANIA experiment for searching for and studying the variability of astrophysical objects with a temporal resolution of 10−6s has been completed. More... -
 Gravitational lenses, known for forming multiple images of distant objects (galaxies and quasars), are often used in modern astrophysics to diagnose the large-scale distribution of matter in the universe. However, the study of the lensed images themselves allows us to examine in more detail the structure of the central parsec of active nuclei, spatially unresolved using direct optical methods. More...
Gravitational lenses, known for forming multiple images of distant objects (galaxies and quasars), are often used in modern astrophysics to diagnose the large-scale distribution of matter in the universe. However, the study of the lensed images themselves allows us to examine in more detail the structure of the central parsec of active nuclei, spatially unresolved using direct optical methods. More... -
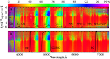 As the decay of the nucleus into fragments is not common in comets, it is observed very rarely. About 40 comets have been observed after their splitting in the last 150 years. The partial fragmentation of the cometary nucleus or its complete disintegration allows us to study the process regarding nucleus mass loss, internal structure, and composition of the nucleus. More...
As the decay of the nucleus into fragments is not common in comets, it is observed very rarely. About 40 comets have been observed after their splitting in the last 150 years. The partial fragmentation of the cometary nucleus or its complete disintegration allows us to study the process regarding nucleus mass loss, internal structure, and composition of the nucleus. More...
2021
-
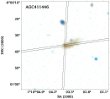 In the framework of the modern cosmological paradigm, the great majority of galaxies have been formed during the first 1-2 Gyr after the Big Bang, which occured 13.7 Gyr ago. Initially, the galaxies were purely gas objects with the so-called "primordial" element composition, comprised of H and He (with mass ratio of ~4:1). More...
In the framework of the modern cosmological paradigm, the great majority of galaxies have been formed during the first 1-2 Gyr after the Big Bang, which occured 13.7 Gyr ago. Initially, the galaxies were purely gas objects with the so-called "primordial" element composition, comprised of H and He (with mass ratio of ~4:1). More... -
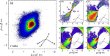 The study of the optical, physical, and chemical properties of dust from small bodies in the Solar system helps us to understand the main mechanisms of their formation and evolution in the protosolar nebula. More...
The study of the optical, physical, and chemical properties of dust from small bodies in the Solar system helps us to understand the main mechanisms of their formation and evolution in the protosolar nebula. More... -
 The subject of this study is a binary system in the galaxy UGC 6456 (also known as VII Zw 403). It is a highly variable source in both the X-ray and optical ranges, which, having a peak X-ray luminosity of Lx = 1.7×1040 erg/s, can be classified as ultraluminous X-ray source (ULXs). More...
The subject of this study is a binary system in the galaxy UGC 6456 (also known as VII Zw 403). It is a highly variable source in both the X-ray and optical ranges, which, having a peak X-ray luminosity of Lx = 1.7×1040 erg/s, can be classified as ultraluminous X-ray source (ULXs). More... -
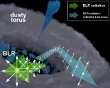 Active galactic nuclei (AGN) are unresolvable with modern optical telescopes since the apparent angular size of the central parsec is ≪ 0.1 arcsec even for the closest active galaxies. This leads to difficulties with methods for estimating distances within the AGN. More...
Active galactic nuclei (AGN) are unresolvable with modern optical telescopes since the apparent angular size of the central parsec is ≪ 0.1 arcsec even for the closest active galaxies. This leads to difficulties with methods for estimating distances within the AGN. More...
2020
-
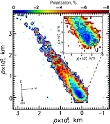 The ice and organics particles in distant comet C/2014 A4 (SONEAR). More...
The ice and organics particles in distant comet C/2014 A4 (SONEAR). More... -
 The Russian RATAN-600 telescope helps to understand the origin of cosmic neutrinos. More...
The Russian RATAN-600 telescope helps to understand the origin of cosmic neutrinos. More...
2019
-
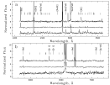 New luminous blue variables (LBV) in star-forming galaxy NGC 4736. More...
New luminous blue variables (LBV) in star-forming galaxy NGC 4736. More... -
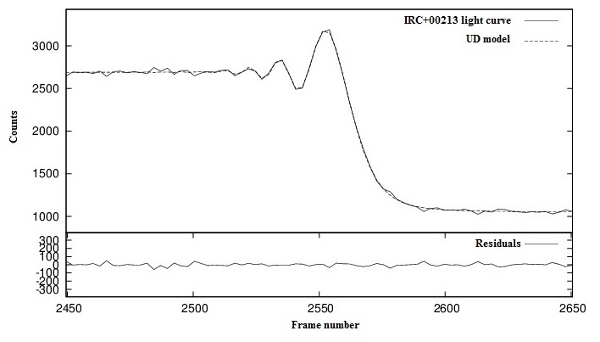 Radius of the M giant IRC+00213 Measured for the First Time. More...
Radius of the M giant IRC+00213 Measured for the First Time. More...
2018
-
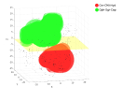 Formation of the Nearby Void catalog and a sample of Galaxies residing in them. More...
Formation of the Nearby Void catalog and a sample of Galaxies residing in them. More... -
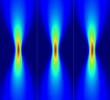 In 2018, we implemented the mode of fast radiometry with a discretization interval from 60 to 490 μs at the 4.7 GHz sensitive radiometer for the first time. More...
In 2018, we implemented the mode of fast radiometry with a discretization interval from 60 to 490 μs at the 4.7 GHz sensitive radiometer for the first time. More... -
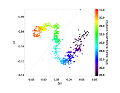 In 2018 February on the 6-m BTA telescope of the SAO RAS we carried out a 9-hour photometric and polarimetric monitoring of S5 0716+714 using the SCORPIO spectrograph. More...
In 2018 February on the 6-m BTA telescope of the SAO RAS we carried out a 9-hour photometric and polarimetric monitoring of S5 0716+714 using the SCORPIO spectrograph. More... -
 Using various techniques of optical observations at the 6-m Russian telescope (direct images, long-slit and 3D spectroscopy), we have studied distribution and motions of the ionized gas in the galaxy Mrk 6 having an active (Seyfert) nucleus. More...
Using various techniques of optical observations at the 6-m Russian telescope (direct images, long-slit and 3D spectroscopy), we have studied distribution and motions of the ionized gas in the galaxy Mrk 6 having an active (Seyfert) nucleus. More... -
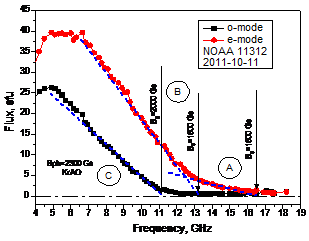 Radiation of the 4th harmonica of the gyro-frequency in the Solar corona above the spot was detected due to detailed spectroscopic observations at RATAN-600 with high-accuracy polarization measurements. More...
Radiation of the 4th harmonica of the gyro-frequency in the Solar corona above the spot was detected due to detailed spectroscopic observations at RATAN-600 with high-accuracy polarization measurements. More...
2017
-
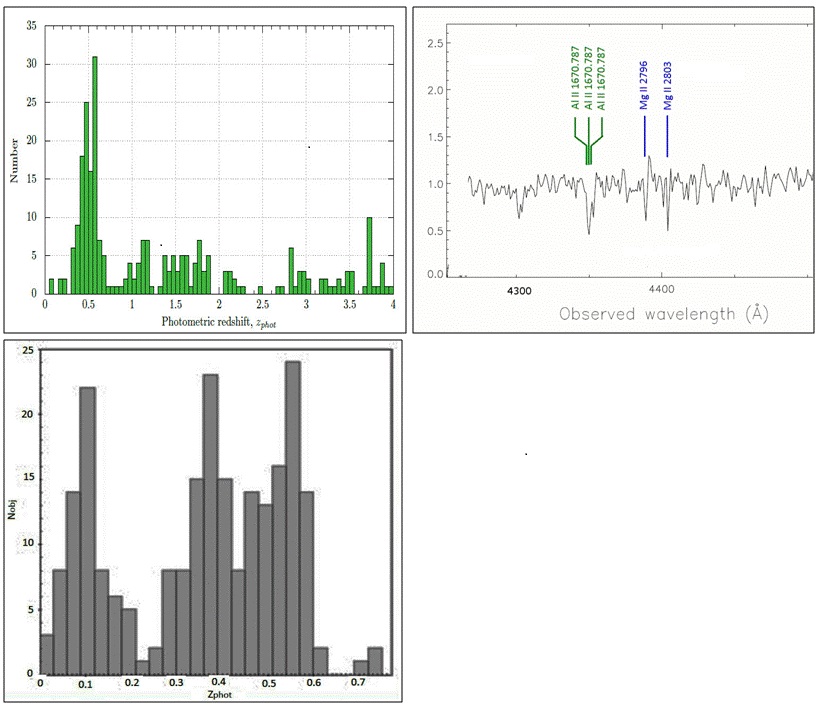 From observations carried out with the telescopes BTA/SCORPIO and VLT/UVES and from data of new catalogs SDSS-III and others, the characteristic signatures of the clustering of field galaxies with a redshift of z ≈ 0.56 around the gamma-ray burst GRB 021004 position were detected. More...
From observations carried out with the telescopes BTA/SCORPIO and VLT/UVES and from data of new catalogs SDSS-III and others, the characteristic signatures of the clustering of field galaxies with a redshift of z ≈ 0.56 around the gamma-ray burst GRB 021004 position were detected. More... -
 In mid-December 2017, the asteroid 3200 Phaethon will make a close approach to the Earth. It is a small asteroid with a diameter of about 5 km. Although its size is quite small in comparison with biggest asteroids of the Solar System, it is one of the largest objects among those crossing the Earth's orbit. More...
In mid-December 2017, the asteroid 3200 Phaethon will make a close approach to the Earth. It is a small asteroid with a diameter of about 5 km. Although its size is quite small in comparison with biggest asteroids of the Solar System, it is one of the largest objects among those crossing the Earth's orbit. More... -
 Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko (hereinafter 67P) was the research target of the Rosetta space mission. Before the Rosetta started, comet 67P had been poorly studied. Thus, its physical properties were obtained as a result of a detailed study within the international campaign of ground-based observations of the comet (2013-2016). More...
Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko (hereinafter 67P) was the research target of the Rosetta space mission. Before the Rosetta started, comet 67P had been poorly studied. Thus, its physical properties were obtained as a result of a detailed study within the international campaign of ground-based observations of the comet (2013-2016). More... -
 Mass and radius are fundamental stellar parameters most complex for measurement. Meanwhile, these parameters are necessary for star modeling and explaining physical processes in them and the evolution of these objects. More...
Mass and radius are fundamental stellar parameters most complex for measurement. Meanwhile, these parameters are necessary for star modeling and explaining physical processes in them and the evolution of these objects. More... -
 We evaluated the quality of flare activity forecasting in active regions based on spectral-polarization observations at RATAN-600 in the wide range of radio waves. More...
We evaluated the quality of flare activity forecasting in active regions based on spectral-polarization observations at RATAN-600 in the wide range of radio waves. More... -
 Evolutionary status of the high-luminous star V1302 Aql (associated with the powerful IR source IRC+10420) has not been determined for a long time. More...
Evolutionary status of the high-luminous star V1302 Aql (associated with the powerful IR source IRC+10420) has not been determined for a long time. More... -
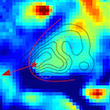 The nature of ultraluminous X-ray sources (ULXs) remains a subject of controversy and debates for past two decades. More...
The nature of ultraluminous X-ray sources (ULXs) remains a subject of controversy and debates for past two decades. More... -
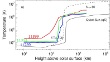 First temperature measurements over active regions have been obtained based on an automatic iterative method applied to the data observed at RATAN-600. More...
First temperature measurements over active regions have been obtained based on an automatic iterative method applied to the data observed at RATAN-600. More...
2016
-
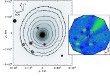 Currently, attempts are underway to establish a taxonomy of comets on the basis of their composition and to link it to the place of their origin. More...
Currently, attempts are underway to establish a taxonomy of comets on the basis of their composition and to link it to the place of their origin. More... -
 Monitoring of the continuum of SETI candidates with RATAN-600 (SAO RAS official comment). More...
Monitoring of the continuum of SETI candidates with RATAN-600 (SAO RAS official comment). More... -
 The on-sky position of GRB 160625B (Dirirsa et al., GCN Circ. 19580) has been observed by Mini-MegaTORTORA nine-channel wide-field monitoring system with high temporal resolution before, during and just after the LAT trigger time (T0 = 2016-06-25 22:43:24). More...
The on-sky position of GRB 160625B (Dirirsa et al., GCN Circ. 19580) has been observed by Mini-MegaTORTORA nine-channel wide-field monitoring system with high temporal resolution before, during and just after the LAT trigger time (T0 = 2016-06-25 22:43:24). More... -
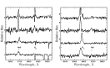 Using optical spectroscopy a nature of ultraluminous X-ray sources in external galaxies whose X-ray luminosities exceed the luminosities of the brightest black holes in our Galaxy by thousands of times was revealed. More...
Using optical spectroscopy a nature of ultraluminous X-ray sources in external galaxies whose X-ray luminosities exceed the luminosities of the brightest black holes in our Galaxy by thousands of times was revealed. More... -
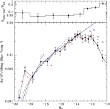 The sample of the Local Volume galaxies (distance smaller than 10 Mpc) gives a unique opportunity to study the properties of galaxies including the weakest objects: the absolute magnitude MB≈−10 and the virial mass Mvir≈109M☼. More...
The sample of the Local Volume galaxies (distance smaller than 10 Mpc) gives a unique opportunity to study the properties of galaxies including the weakest objects: the absolute magnitude MB≈−10 and the virial mass Mvir≈109M☼. More... -
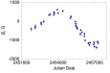 Based on the magnetic field measurements of the chemically peculiar star HD 965, conducted in 2000-2015 with the SAO RAS 6-m telescope, we have found that this object is an ultra slow magnetic rotator with a rotation period of about 20 years. The obtained result is strong evidence in favor of the so-called fossil theory of large-scale field formation in these objects. More...
Based on the magnetic field measurements of the chemically peculiar star HD 965, conducted in 2000-2015 with the SAO RAS 6-m telescope, we have found that this object is an ultra slow magnetic rotator with a rotation period of about 20 years. The obtained result is strong evidence in favor of the so-called fossil theory of large-scale field formation in these objects. More... -
 On the detection of gravitational waves by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Obsevatory (LIGO). More...
On the detection of gravitational waves by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Obsevatory (LIGO). More... -
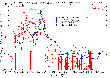 The Galactic low-mass X-ray binary GS 2023+338 was discovered during the burst on May 22, 1989 with the Japanise satellite Ginga (aka Galaxy). The flux reached 17 crabs (this unit of flux measurement is an bright X-ray source, Crab Nebula) at 10-35 keV. More...
The Galactic low-mass X-ray binary GS 2023+338 was discovered during the burst on May 22, 1989 with the Japanise satellite Ginga (aka Galaxy). The flux reached 17 crabs (this unit of flux measurement is an bright X-ray source, Crab Nebula) at 10-35 keV. More... -
Variability of emission at scales from fractions of a second to tens of years is one of characteristic properties of different celestial objects. Transient events are also the emission variability though not regularly observed. Such events are difficult to detect for that reason. During the analysis of the surveys carried out on RATAN-600, it was found that almost one fifth of the detected sources shows significant radio flux variations. We discovered three radio transients in our search. More...
2015
-
 Currently, there is very little information on comets which are active beyond the orbit of Jupiter. Dust tails and comas of such comets are observed at large distances from the Sun (greater than 5 au), where water ice sublimation is inconsiderable. More...
Currently, there is very little information on comets which are active beyond the orbit of Jupiter. Dust tails and comas of such comets are observed at large distances from the Sun (greater than 5 au), where water ice sublimation is inconsiderable. More... -
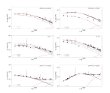 Two new LBV stars have been discovered in the Andromeda Galaxy. Since the middle of the last century, only four such objects had been known in this galaxy, they were discovered by American scientists Edwin Hubble and Allan Sandage with colleagues. Astronomers from SAO added two more stars to this list in 2015. More...
Two new LBV stars have been discovered in the Andromeda Galaxy. Since the middle of the last century, only four such objects had been known in this galaxy, they were discovered by American scientists Edwin Hubble and Allan Sandage with colleagues. Astronomers from SAO added two more stars to this list in 2015. More... -
 The March 20 total solar eclipse was visible over the North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans. The partial phases were observed in Europe, the western regions of Russia, Central Asia, the Middle East and partially in the North Africa. In the Special Astrophysical Observatory it was also partial with the Moon coverage of the Sun of less than 40%. More...
The March 20 total solar eclipse was visible over the North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans. The partial phases were observed in Europe, the western regions of Russia, Central Asia, the Middle East and partially in the North Africa. In the Special Astrophysical Observatory it was also partial with the Moon coverage of the Sun of less than 40%. More... -
 In January 2015 using the Mini-MegaTORTORA multichannel optical sky-monitoring system with subsecond temporal resolution, the observations of comet C/2014 Q2 (Lovejoy) and asteroid 357439 2004 BL86 were carried out. More...
In January 2015 using the Mini-MegaTORTORA multichannel optical sky-monitoring system with subsecond temporal resolution, the observations of comet C/2014 Q2 (Lovejoy) and asteroid 357439 2004 BL86 were carried out. More...
2014
-
 Our recent observations with the Hubble Space Telescope (August 29, 2014) led to revealing a highly isolated dwarf spheroidal galaxy KKs 3 situated at a distance of 2.12±0.07 Mpc from the Milky Way. The dSph galaxy locates on the southern sky (RA = 02h24m44.4s, Dec. = −73°30′51″, J2000.0) and has a stellar mass about 1/10000 of the Milky Way mass. More...
Our recent observations with the Hubble Space Telescope (August 29, 2014) led to revealing a highly isolated dwarf spheroidal galaxy KKs 3 situated at a distance of 2.12±0.07 Mpc from the Milky Way. The dSph galaxy locates on the southern sky (RA = 02h24m44.4s, Dec. = −73°30′51″, J2000.0) and has a stellar mass about 1/10000 of the Milky Way mass. More... -
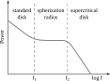 SS433 is a close binary system, one star is a supergiant, a second one is a black hole. The supergiant's matter overflows to the neighbouring black hole and floods the hole with a powerful mass flux: 6 millions of billions tons per second (that is one Earth mass for 11 days). Even a black hole cannot accept such an enormous mass flux, a supercritical accretion disk appears. More...
SS433 is a close binary system, one star is a supergiant, a second one is a black hole. The supergiant's matter overflows to the neighbouring black hole and floods the hole with a powerful mass flux: 6 millions of billions tons per second (that is one Earth mass for 11 days). Even a black hole cannot accept such an enormous mass flux, a supercritical accretion disk appears. More... -
 The variability of the spectrum of the optical component of the IR-source IRAS 01005+7910 was discovered for the first time in the BTA spectra. Long-term monitoring of the object was carried out during 2002-2013 with a high spectral resolution (R = 60000). More...
The variability of the spectrum of the optical component of the IR-source IRAS 01005+7910 was discovered for the first time in the BTA spectra. Long-term monitoring of the object was carried out during 2002-2013 with a high spectral resolution (R = 60000). More... -
 Astronomers of the SAO together with an international group of scientists have proposed an explanation to the long-standing mystery of why magnetic fields are more common amongst cool white dwarf stars than amongst young and hotter ones. More...
Astronomers of the SAO together with an international group of scientists have proposed an explanation to the long-standing mystery of why magnetic fields are more common amongst cool white dwarf stars than amongst young and hotter ones. More... -
 According to the most popular cosmological paradigm, the greater part of the galaxy mass is accumulated in the dark matter halo. The mass value can be measured in terms of various model assumptions, analyzing the available observational data, for example, the distribution of the rotation velocity at large distances from the center (the rotation curve). It is much more difficult to make an estimate of the shape of the dark halo in a particular galaxy, i.e. to understand whether it is spherical, flattened or triaxial. More...
According to the most popular cosmological paradigm, the greater part of the galaxy mass is accumulated in the dark matter halo. The mass value can be measured in terms of various model assumptions, analyzing the available observational data, for example, the distribution of the rotation velocity at large distances from the center (the rotation curve). It is much more difficult to make an estimate of the shape of the dark halo in a particular galaxy, i.e. to understand whether it is spherical, flattened or triaxial. More... -
 SAO researchers have discovered that supercritical accretion disks eject hot gas with a velocity of a few thousand kilometers per second. The supercritical regime of accretion onto black holes is very important for astrophysics. In the first half-billion years just after our Universe was born, supermassive black holes (quasars) began to appear and grow in centers of young galaxies. More...
SAO researchers have discovered that supercritical accretion disks eject hot gas with a velocity of a few thousand kilometers per second. The supercritical regime of accretion onto black holes is very important for astrophysics. In the first half-billion years just after our Universe was born, supermassive black holes (quasars) began to appear and grow in centers of young galaxies. More... -
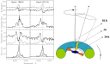 A unique set of linear polarization measurements in the spectrum of the Seyfert galaxy Mkn 6 was obtained with the 6-meter telescope. It was shown for the first time that the analysis of the polarization angle dependence on the velocity across the hydrogen line profiles due to the gas emission in the broad-line formation region near the massive AGN allows to determine directly from observations the type of motion in the broad-line formation region, which in the case of Mkn 6 turned out to be Keplerian at distances less than 0.02 pc from the nucleus. The lower mass limit determined for the supermassive black hole in the center of the Mkn 6 galaxy is equal to 150 million solar masses. More...
A unique set of linear polarization measurements in the spectrum of the Seyfert galaxy Mkn 6 was obtained with the 6-meter telescope. It was shown for the first time that the analysis of the polarization angle dependence on the velocity across the hydrogen line profiles due to the gas emission in the broad-line formation region near the massive AGN allows to determine directly from observations the type of motion in the broad-line formation region, which in the case of Mkn 6 turned out to be Keplerian at distances less than 0.02 pc from the nucleus. The lower mass limit determined for the supermassive black hole in the center of the Mkn 6 galaxy is equal to 150 million solar masses. More... -
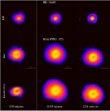 High spectral resolution echelle spectroscopy of supergiants at the post-ABG stage resulted in the formation of a sample of these objects possessing a high infrared excess, an emission at 21 μm, and also large overabundances of carbon and heavy metals, synthesized by the s-process at the preceding AGB stage. More...
High spectral resolution echelle spectroscopy of supergiants at the post-ABG stage resulted in the formation of a sample of these objects possessing a high infrared excess, an emission at 21 μm, and also large overabundances of carbon and heavy metals, synthesized by the s-process at the preceding AGB stage. More...
2013
-
 Among the newly observed objects, we discovered the galaxies UGC 2172 and NGC 3239 in the stage of a vigorous burst of star formation. More...
Among the newly observed objects, we discovered the galaxies UGC 2172 and NGC 3239 in the stage of a vigorous burst of star formation. More... -
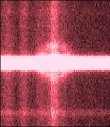 The spatially resolved structure near the hydrogen emission Hα line was found in the spectrum taken with the BTA/SCORPIO in June, 2013. It extendeds by 6.5 arcsec along the frame vertical, and by 2600 km/s (radial velocity) along the centre line of the frame. The structure has been formed by an empty spherical shell that has erupted during the outburst 13.5 years ago, and is now expanding with the velocity of 1300 km/s. The expansion velocity of 0.24 arcsec/yr corresponds to the distance to the nova of 1.2±0.2 kpc. More...
The spatially resolved structure near the hydrogen emission Hα line was found in the spectrum taken with the BTA/SCORPIO in June, 2013. It extendeds by 6.5 arcsec along the frame vertical, and by 2600 km/s (radial velocity) along the centre line of the frame. The structure has been formed by an empty spherical shell that has erupted during the outburst 13.5 years ago, and is now expanding with the velocity of 1300 km/s. The expansion velocity of 0.24 arcsec/yr corresponds to the distance to the nova of 1.2±0.2 kpc. More...
2012
-
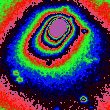 An estimate the rotation period of cometary nuclei is important for understanding and describing the physical processes of the cometary activity. Unfortunately, the measurements of the rotation periods of the comet nucleus depend on the model assumptions and it is one of the main reasons for the scatter of the estimates given in various articles for a given comet. More...
An estimate the rotation period of cometary nuclei is important for understanding and describing the physical processes of the cometary activity. Unfortunately, the measurements of the rotation periods of the comet nucleus depend on the model assumptions and it is one of the main reasons for the scatter of the estimates given in various articles for a given comet. More... -
 Ultraluminous X-ray sources (ULXs) are located in external galaxies, their X-ray luminosities are thousand times greater than those of brightest black holes in the Galaxy. It has been found in the VLT and BTA observations of extragalactic stellar clusters related to the ULXs, that these objects are stellar-mass black holes with supercritical accretion disks. More...
Ultraluminous X-ray sources (ULXs) are located in external galaxies, their X-ray luminosities are thousand times greater than those of brightest black holes in the Galaxy. It has been found in the VLT and BTA observations of extragalactic stellar clusters related to the ULXs, that these objects are stellar-mass black holes with supercritical accretion disks. More... -
 Recent studies indicate that stars are most likely forming within the binary and multiple systems. In our Galaxy, according to various estimates, at least 50 percent of stars have companions. Therefore, the study of binary and multiple stars is important for understanding the mechanisms of star formation in general. More...
Recent studies indicate that stars are most likely forming within the binary and multiple systems. In our Galaxy, according to various estimates, at least 50 percent of stars have companions. Therefore, the study of binary and multiple stars is important for understanding the mechanisms of star formation in general. More... -
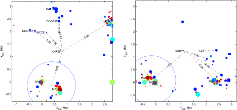 We present a photometric and spectroscopic study of the unique isolated nearby galaxy KKR25. More...
We present a photometric and spectroscopic study of the unique isolated nearby galaxy KKR25. More... -
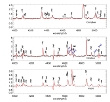 We find a transition of LBV star from the LBV instability strip to the region of classical WN for the first time. More...
We find a transition of LBV star from the LBV instability strip to the region of classical WN for the first time. More... -
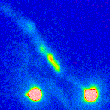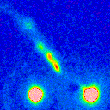 The HH flow associated with young stellar object HL Tau has an exciting history and even until now the origin of some its features is not clear yet. Flow starts as the relatively faint and narrow jet from HL Tau but at distance of about 20″ from the star it abruptly changes direction by about 14 deg and becomes much brighter and appears complex knotty morphology. More...
The HH flow associated with young stellar object HL Tau has an exciting history and even until now the origin of some its features is not clear yet. Flow starts as the relatively faint and narrow jet from HL Tau but at distance of about 20″ from the star it abruptly changes direction by about 14 deg and becomes much brighter and appears complex knotty morphology. More...
2011
-
 Galaxies with polar rings (PRGs) are a unique class of extragalactic objects, consisting of a ring or disk of gas, stars and dust orbiting in a plane nearly perpendicular to the disk of a central galaxy. More...
Galaxies with polar rings (PRGs) are a unique class of extragalactic objects, consisting of a ring or disk of gas, stars and dust orbiting in a plane nearly perpendicular to the disk of a central galaxy. More... -
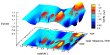 The results of long-term monitoring of Gigahertz-Peaked Spectrum sources were found the statistically significant differences (0.05 significance level) in the high-frequency spectral index distribution between subgroups of galaxies and quasars. More...
The results of long-term monitoring of Gigahertz-Peaked Spectrum sources were found the statistically significant differences (0.05 significance level) in the high-frequency spectral index distribution between subgroups of galaxies and quasars. More... -
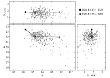 According to modern views on the evolution and origin of stars, most of the stars are members of binary systems. If both components are massive enough, they eventually go supernova one by one, whereas their cores collapse, turning into black holes or neutron stars. More...
According to modern views on the evolution and origin of stars, most of the stars are members of binary systems. If both components are massive enough, they eventually go supernova one by one, whereas their cores collapse, turning into black holes or neutron stars. More... -
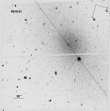 The history of star formation was successfully analyzed for the first time based on the spectra of the stellar population of dwarf galaxies of low surface brightness outside the Local Group. We have investigated the stellar population of two dwarf spheroidal galaxies KDG61 and KDG64 in the central part of a close group of galaxies M81. More...
The history of star formation was successfully analyzed for the first time based on the spectra of the stellar population of dwarf galaxies of low surface brightness outside the Local Group. We have investigated the stellar population of two dwarf spheroidal galaxies KDG61 and KDG64 in the central part of a close group of galaxies M81. More... -
 Solar flare activity is produced by the processes of accumulation and release of energy in an active region. A complex magnetic structure is formed over the spots, the reconnection of which leads to the generation of a flare. The information about the magnetic field can be retrieved from is polarized microwave radiation, the spectrum of which is correlated with the flare activity. More...
Solar flare activity is produced by the processes of accumulation and release of energy in an active region. A complex magnetic structure is formed over the spots, the reconnection of which leads to the generation of a flare. The information about the magnetic field can be retrieved from is polarized microwave radiation, the spectrum of which is correlated with the flare activity. More... -
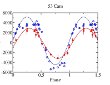 As a result of BTA observations of 23 chemically peculiar stars with strong magnetic fields, it was found that in 22 of them the longitudinal magnetic field, measured from the hydrogen line cores are considerably lower (by about 1/3) than the value measured from metal lines in the same spectra. More...
As a result of BTA observations of 23 chemically peculiar stars with strong magnetic fields, it was found that in 22 of them the longitudinal magnetic field, measured from the hydrogen line cores are considerably lower (by about 1/3) than the value measured from metal lines in the same spectra. More...
2010
-
 According to the current estimates, a few percent of Main Sequence B5-F5 stars reveal strong surface magnetic fields reaching the values of tens of kilogauss, which is an order of magnitude greater than the maximal magnetic field in sunspots. More...
According to the current estimates, a few percent of Main Sequence B5-F5 stars reveal strong surface magnetic fields reaching the values of tens of kilogauss, which is an order of magnitude greater than the maximal magnetic field in sunspots. More... -
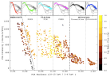 The close X-ray binary with relativisic jest, contained probably a black hole, Cygnus X-3 has been detected in first time in Gamma-rays at enegries higher 100 MeV (AGILE, Tavani et al., Nature, 2009) during the intense radio flares, monitored with RATAN-600 radio telecope. More...
The close X-ray binary with relativisic jest, contained probably a black hole, Cygnus X-3 has been detected in first time in Gamma-rays at enegries higher 100 MeV (AGILE, Tavani et al., Nature, 2009) during the intense radio flares, monitored with RATAN-600 radio telecope. More... -
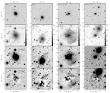 By means of deep optical images obtained at the Special Astrophysical Observatory 6-m telescope it was discovered that some Seyfert galaxies that were earlier considered to be non-interacting objects displayed signatures of elongated tidal envelopes belonging to satellite debris. More...
By means of deep optical images obtained at the Special Astrophysical Observatory 6-m telescope it was discovered that some Seyfert galaxies that were earlier considered to be non-interacting objects displayed signatures of elongated tidal envelopes belonging to satellite debris. More... -
 CH Cyg is one of the most fascinating as well as the brightest and closest symbiotic stars. It's composed of an M7 giant and a hot companion, most likely an accreting white dwarf. More...
CH Cyg is one of the most fascinating as well as the brightest and closest symbiotic stars. It's composed of an M7 giant and a hot companion, most likely an accreting white dwarf. More... -
 A bright extended nebulosity around a lenticular galaxy NGC 4460 was discovered by Igor Karachentsev and Serafim Kaisin (2008, A&A, 479, 603) during the recent Hα survey of nearby galaxies on the SAO RAS 6-m telescope. More...
A bright extended nebulosity around a lenticular galaxy NGC 4460 was discovered by Igor Karachentsev and Serafim Kaisin (2008, A&A, 479, 603) during the recent Hα survey of nearby galaxies on the SAO RAS 6-m telescope. More... -
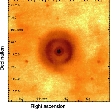 In the spectral observations of stars with infrared circular nebulae, found in the Spitzer survey (24 microns), a new LBV star was discovered in the Galaxy. More...
In the spectral observations of stars with infrared circular nebulae, found in the Spitzer survey (24 microns), a new LBV star was discovered in the Galaxy. More...
2009
-
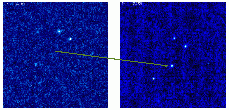 The brightest of all GRBs known to date, GRB 080319B, the "Naked-Eye Burst", has been observed by our colleagues who acquired its detailed optical light curve during the stage of gamma emission. More...
The brightest of all GRBs known to date, GRB 080319B, the "Naked-Eye Burst", has been observed by our colleagues who acquired its detailed optical light curve during the stage of gamma emission. More... -
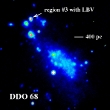 Dwarf galaxy DDO 68 is the closest to us galaxy (D = 10 Mpc) with the lowest metal content known to date. In this galaxy, using the 6 m BTA telescope, a new massive blue variable star with high luminosity (≥105 Sun's luminocities in visible light) was found. More...
Dwarf galaxy DDO 68 is the closest to us galaxy (D = 10 Mpc) with the lowest metal content known to date. In this galaxy, using the 6 m BTA telescope, a new massive blue variable star with high luminosity (≥105 Sun's luminocities in visible light) was found. More... -
 New observations of the RC J0311+0507 radio source using the MERLIN radio interferometer (UK) and the 6-m optical telescope, have added new strokes to the "portrait" of this unusual object, — one of the most powerful and distant radio galaxies (z = 4.51), and raised new questions about the origin of the first galaxies in the early Universe. More...
New observations of the RC J0311+0507 radio source using the MERLIN radio interferometer (UK) and the 6-m optical telescope, have added new strokes to the "portrait" of this unusual object, — one of the most powerful and distant radio galaxies (z = 4.51), and raised new questions about the origin of the first galaxies in the early Universe. More... -
 A new bright LBV (Luminous Blue Variable) star was found in M33 galaxy. More...
A new bright LBV (Luminous Blue Variable) star was found in M33 galaxy. More... -
 The most metal-poor system of four subdwarfs discovered in the solar neighbourhood. More...
The most metal-poor system of four subdwarfs discovered in the solar neighbourhood. More... -
 Identification and Early Spectroscopic Observations of the Optical Transient GRB090726. More...
Identification and Early Spectroscopic Observations of the Optical Transient GRB090726. More...

